Java Exceptions
An exception is an event that occurs during the execution of a program that disrupts the normal flow of instructions during the execution of a program. Exceptions are objects that represent errors that may occur in a Java program. An exception is a condition that is caused by a run-time error in the program.
Exception Handling
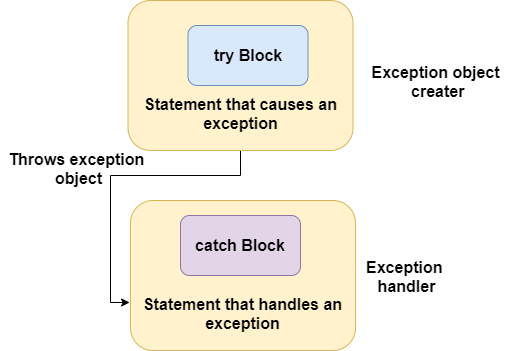
The purpose of the exception handling mechanism is to provide a means to detect and report an "exceptional circumstance" to take appropriate action. The mechanism that suggests incorporation of a separate error handling code that performs the following tasks:
- Find the problem ( Hit the exception)
- Inform that an error has occurred ( Throw the exception )
- Receive the error information ( Catch the exception )
- Take corrective actions ( Handle the exception )
syntax:
..........
..........
try
{
statement; // generates an exception
}
catch (Exception-type e)
{
statement; // processes the exception
}
..........
..........
Example:
class ExeceptionExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 10;
int b = 5;
int c = 5;
int x, y;
try {
x = a / (b - c); // generates an exception
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("Division by zero"); // processes the exception
}
y = a / (b + c);
System.out.println("y = " + y;
}
}
/*OUTPUT:
Division by zero
y = 1 */




